Pythagoras Theorem







Pythagoras Theorem
Pythagoras Theorem:
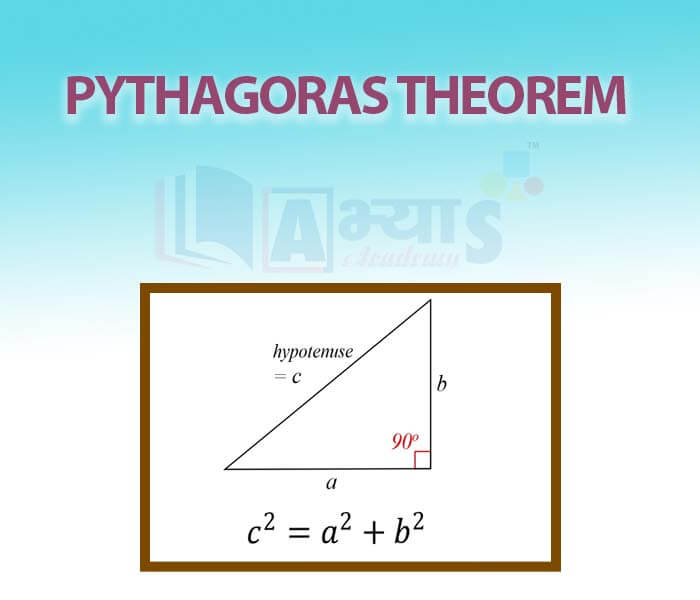
It is the triangle with one of its angles as a right angle, that is, 90 degrees. The side that is opposite to the 90 degree angle is known as the hypotenuse. The other two sides that are adjacent to the right angle are called legs of the triangle.
The theorem, also known as the Pythagorean theorem, states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the lengths of other two sides of the right-angled triangle. Or, the sum of the squares of the two legs of a right triangle is equal to the square of its hypotenuse.
Let us call one of the legs on which the triangle rests as its base. The side opposite to the right angle is its hypotenuse, as we already know. The remaining side is called the perpendicular. So, mathematically, we represent the Pythagoras theorem as:

Example: Find the hypotenuse of a triangle whose lengths of two sides are 4 cm and 10cm.
Solution: Using the Pythagoras theorem,
=102+42=116
Hypotenuse= =10.77cm
Hence the hypotenuse of the triangle is 10.77 cm.
In a right angle triangle ABC, right angled at B , AB = 6cm , BC = 8cm , then AC = _________________ . | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 37 cm long. If one of the remaining two sides is 12 cm in length, then the length of the other side is | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
A man goes 150 m due east and then 200 m due north. How far is he from the starting point?
| |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
About Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

